Unveiling Unsupervised Learning: A Comprehensive Guide

Understanding the Basics
Unsupervised learning is a type of machine learning where an algorithm learns patterns from unlabeled data. It discovers hidden structures and relationships without explicit guidance.
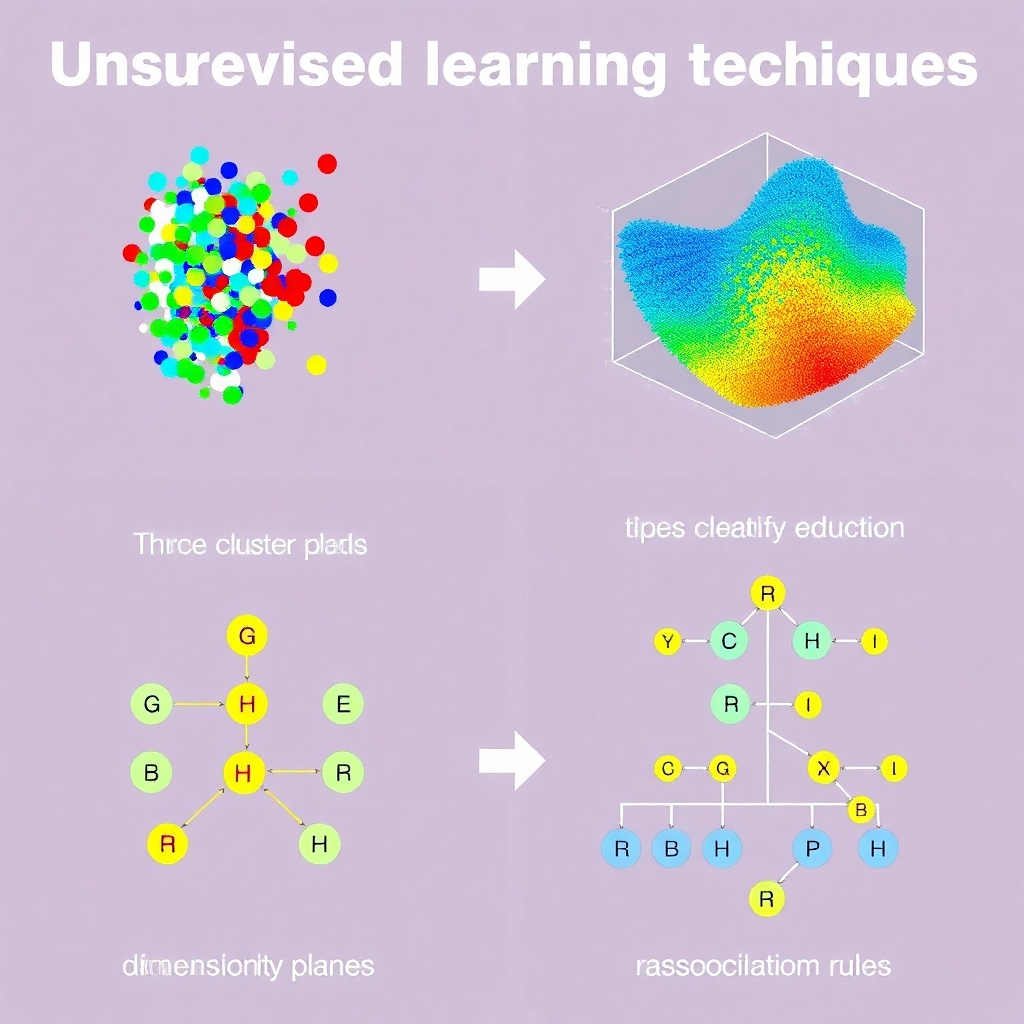
Key Techniques
Common techniques include clustering (grouping similar data points), dimensionality reduction (simplifying data), and association rule mining (discovering relationships between variables).
Real-world Applications
Unsupervised learning is used in customer segmentation, anomaly detection, and recommendation systems, among other applications. It helps businesses understand their data better and make more informed decisions.
Unsupervised Learning Explained: Techniques and Applications
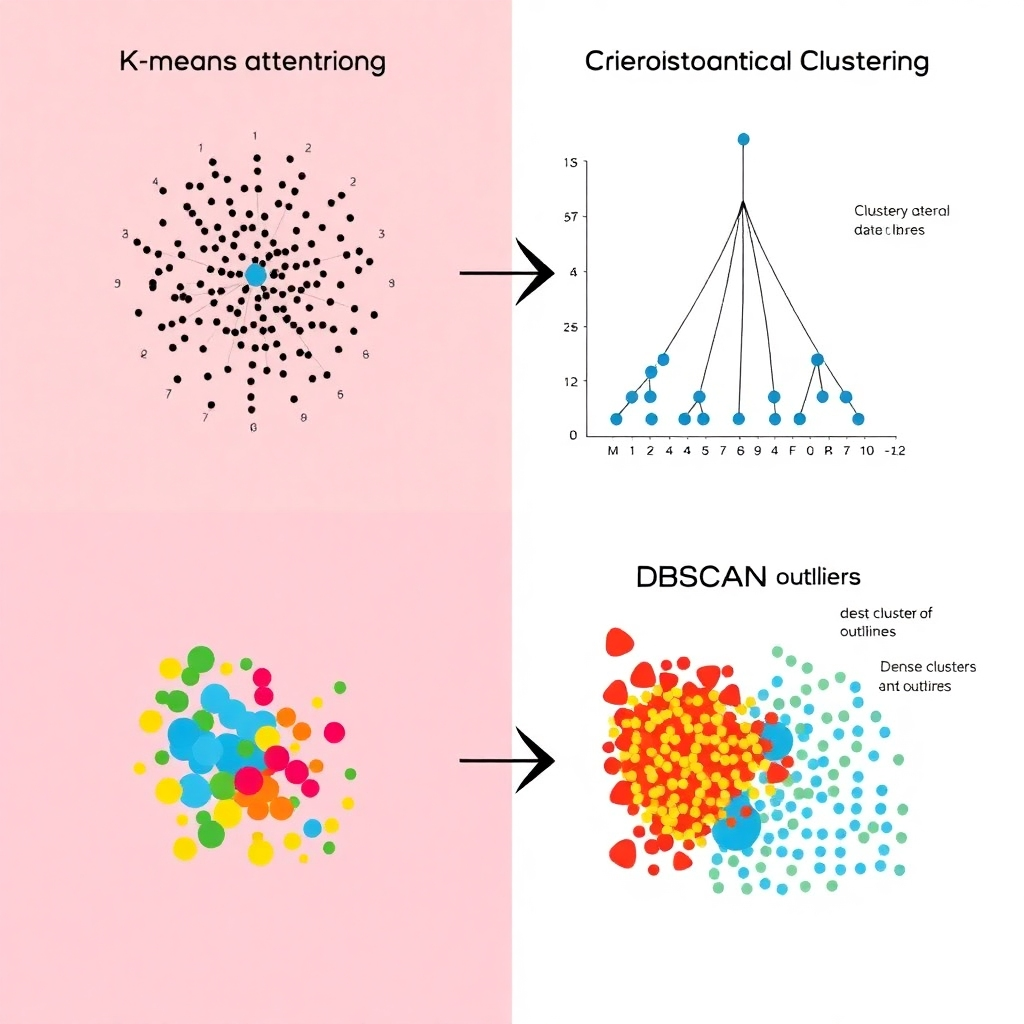
Clustering Algorithms
K-means, hierarchical clustering, and DBSCAN are popular clustering algorithms used to group similar data points together, revealing underlying structure in datasets.
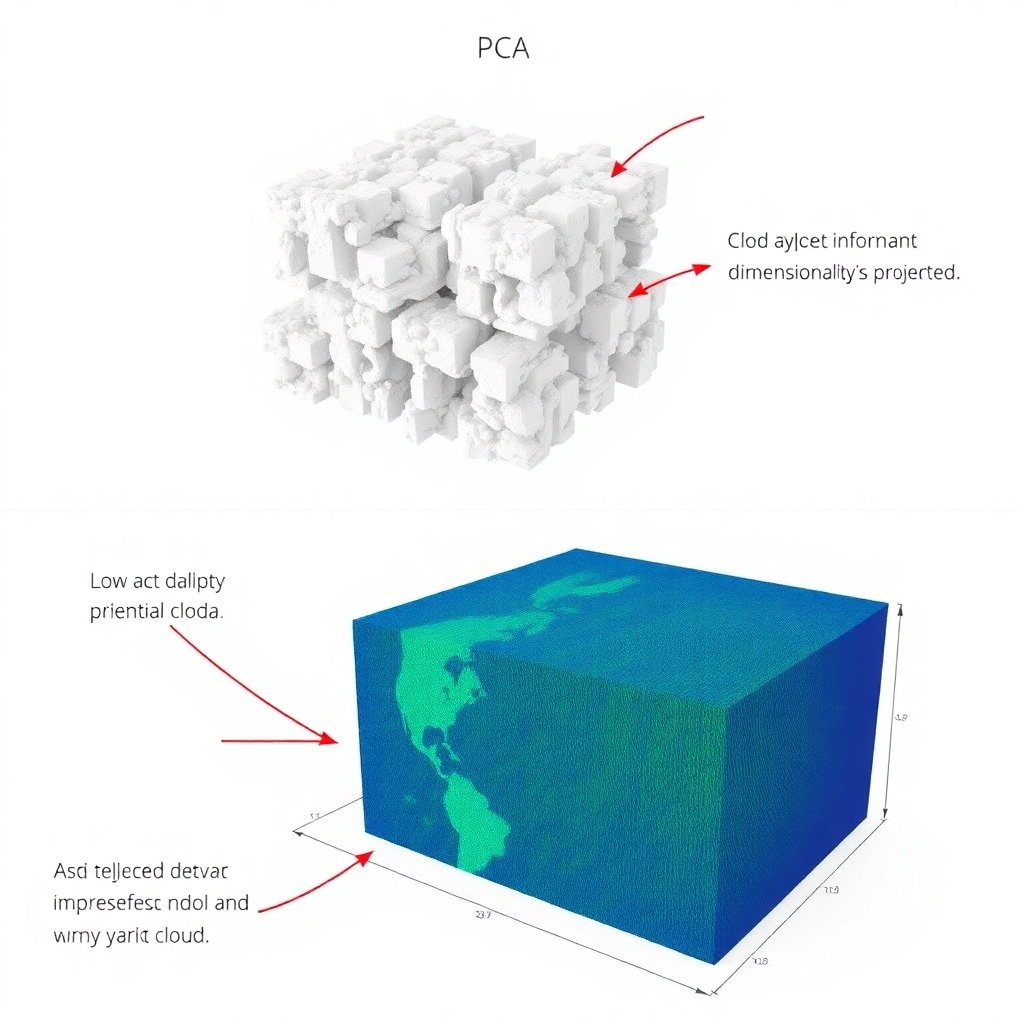
Dimensionality Reduction
Techniques like PCA and t-SNE reduce the number of variables while preserving important information, simplifying data visualization and analysis.

Applications in various fields
From recommendation systems to anomaly detection in cybersecurity, unsupervised learning plays a crucial role in various fields, offering valuable insights from unlabeled data.
Mastering Unsupervised Learning: From Concepts to Implementation
Choosing the Right Algorithm
Selecting the appropriate algorithm depends on the dataset's characteristics and the desired outcome. Factors like data size, structure, and the nature of the patterns influence this choice.
Evaluating Model Performance
Metrics like silhouette score for clustering and reconstruction error for dimensionality reduction help evaluate the effectiveness of the chosen unsupervised learning model.
Practical Implementation
Hands-on exercises and real-world examples guide users through implementing unsupervised learning techniques using popular programming languages like Python and R.