Understanding Supervised Learning: A Comprehensive Guide

The Fundamentals
Supervised learning is a type of machine learning where an algorithm learns from a labeled dataset, meaning each data point is tagged with the correct answer. This allows the algorithm to map inputs to outputs and make predictions on new, unseen data.

Key Algorithms
Popular supervised learning algorithms include linear regression, logistic regression, support vector machines (SVMs), decision trees, and random forests. Each algorithm has its strengths and weaknesses, making the choice dependent on the specific problem and dataset.

Real-World Applications
Supervised learning powers various applications, from spam filters and medical diagnosis to fraud detection and self-driving cars. Its ability to learn from labeled data allows it to accurately predict outcomes in diverse real-world scenarios.
Supervised Learning Explained: Algorithms, Techniques & Applications
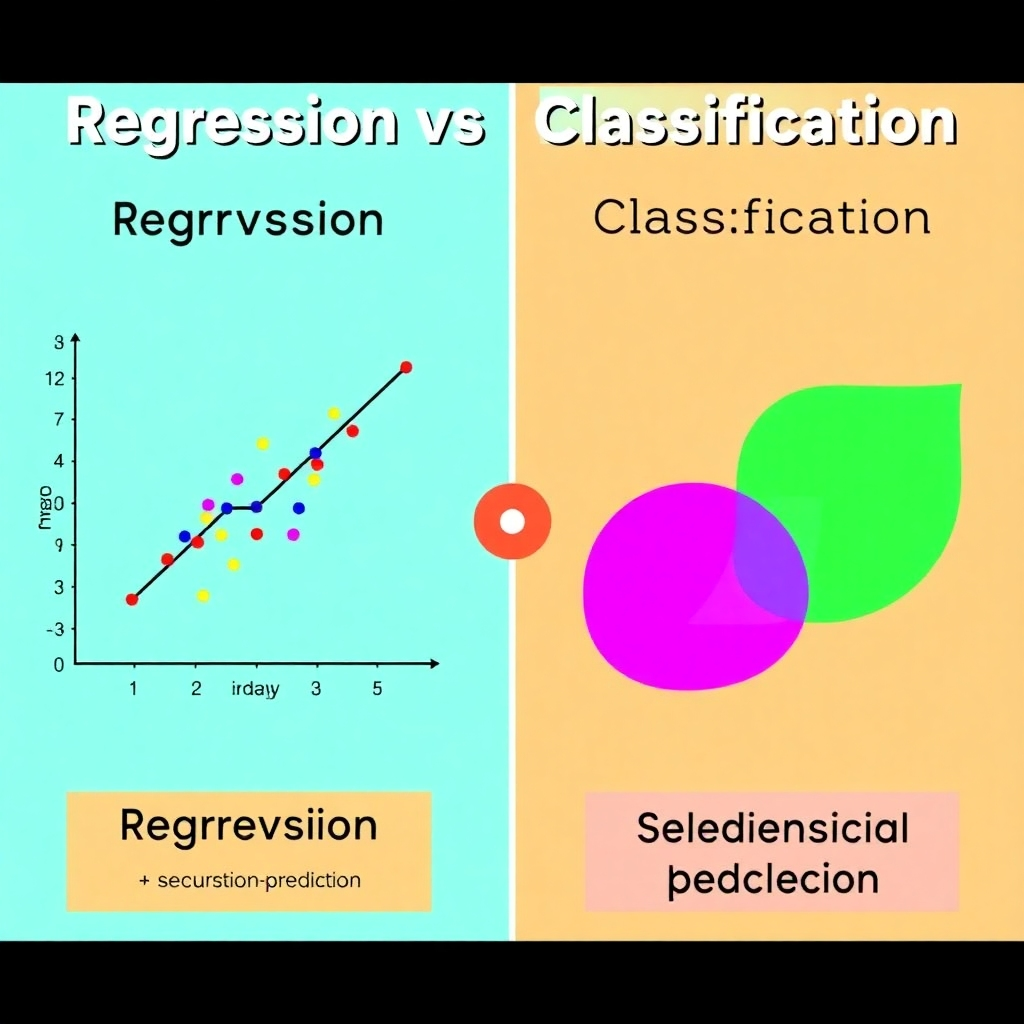
Regression and Classification
Supervised learning is broadly categorized into regression and classification. Regression predicts continuous values (like house prices), while classification predicts categorical values (like spam or not spam).
Model Evaluation Metrics
Accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score are essential metrics used to evaluate supervised learning models. Choosing the right metrics depends on the specific problem and the relative costs of different types of errors.

Advanced Techniques
Ensemble methods, like bagging and boosting, combine multiple models to improve prediction accuracy and robustness. These techniques are powerful but require careful consideration of computational resources.
What is Supervised Learning? A Simple Introduction for Beginners

Learning from Examples
Imagine teaching a child to identify cats and dogs. You'd show them many pictures, labeling each as either a cat or a dog. Supervised learning works similarly; it learns from labeled data.
Predicting Outcomes
Once trained on labeled data, a supervised learning model can predict the outcome for new, unseen data. For instance, it could predict whether a new email is spam or not.

Simple Analogy
Think of it like learning to ride a bike. You learn by practicing and receiving feedback (labeled data). Over time, you get better at riding (improved predictions).